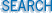
Using Relative Paths for VMD File Definitions |
If you want to ensure that all VMD files that your Iguana server uses are contained in the same directory as the configuration file and the data, you must use a relative path to specify the location of any VMD file used in a channel definition.
By default, if you do not specify the complete path when defining the location of a VMD file, Iguana uses its working directory as a starting point, and then determines the location of the VMD file relative to this working directory. If you have not explicitly defined a working directory, Iguana uses its installation directory as the working directory (such as C:\Program Files\iNTERFACEWARE\Iguana).
For example, consider the following LLP Listener component definition:
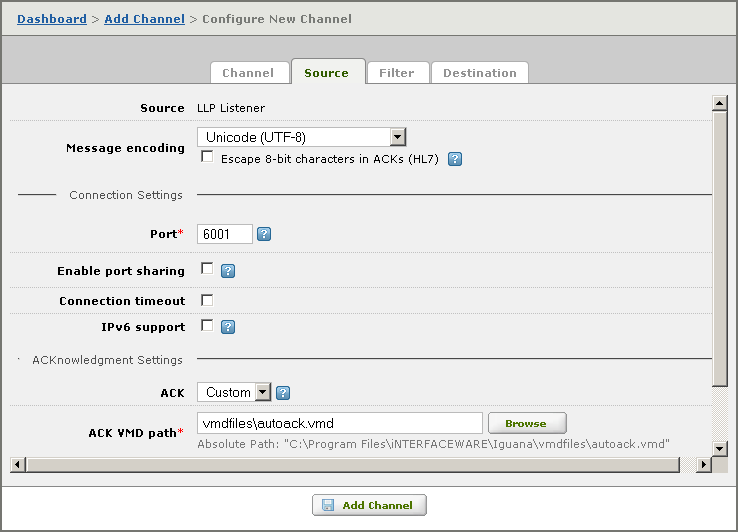
In this example, the location of the VMD file in the ACK VMD path field is specified by the relative path vmdfiles\autoack.vmd. If the Iguana working directory is D:\build\v3, the server will look for the VMD file in D:\build\v3\vmdfiles\autoack.vmd.
If you specify relative paths for all of your VMD files, you can ensure that any version of Iguana that is contained in a directory only uses VMD files that are stored in that directory.
|
The simplest solution is to locate all VMD files in the same directory as the IguanaConfiguration.xml configuration file. This means that all path names specified in channel definitions simply have to include the name of the VMD file: 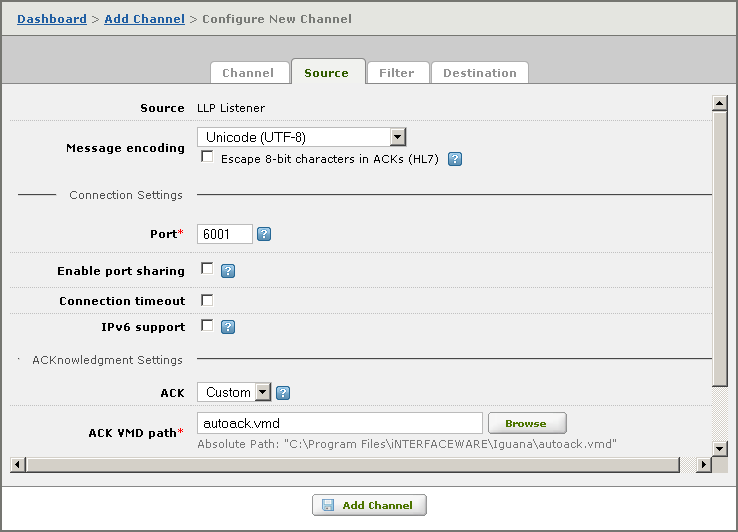 In an LLP Listener channel source component, the default is to assume that the VMD file is in the same directory as the configuration file. Another solution is to use an environment variable to specify the directory in which the VMD files are stored: 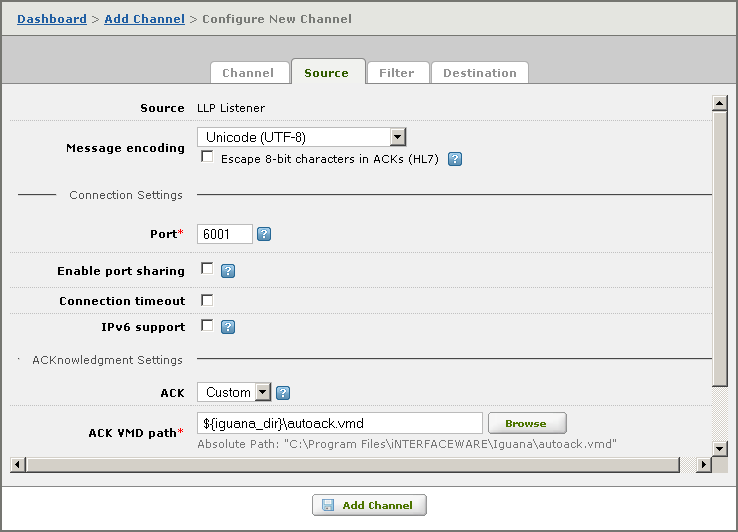 This example uses iguana_dir, an environment variable defined by Iguana, whose value is the location of the directory in which Iguana is installed. | ||
 |