Editing an Environment Variable |
When using Iguana, you can edit any environment variable that is defined on your system. This edit affects only the Iguana server in which you have edited the variable. Other processes on your system are not affected.
To edit an environment variable:
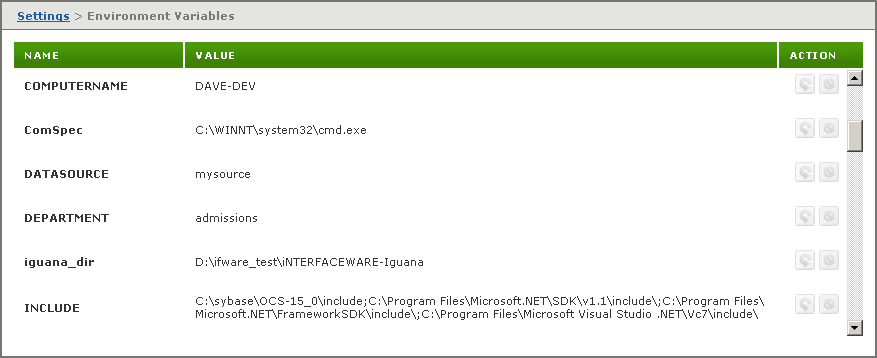
- Click the Settings tab at the top right of the screen. In the Settings screen, click Environment Variables. The Environment Variables screen appears:
- Locate the environment variable that you want to edit and click it. The environment variable and its value are displayed in editable text fields:
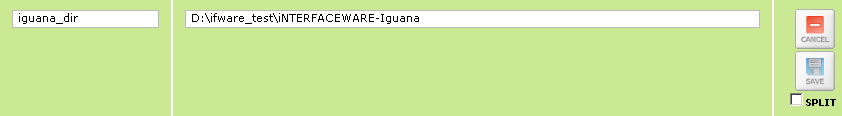
- In the text field in the first column (the Name column), change the name of the environment variable as needed. This name can contain any character that is not a whitespace character. (Examples of whitespace characters include spaces and tabs.)
- In the text field in the second column (the Value column), change the value of the environment variable as needed. A value can contain any character.
- Click
 to save your changes, or click
to save your changes, or click  to cancel editing.
to cancel editing.
If the value of the environment variable consists of one or more subvalues, such as the INCLUDE environment variable shown below, Iguana displays each subvalue on a separate line, and selects the SPLIT check box to indicate that the value of the environment variable has been split:
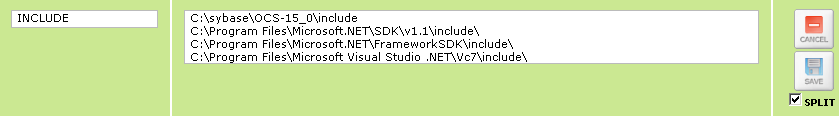
To add a new subvalue, position your cursor at the end of the last subvalue and press Enter. The text field is expanded to make room for the new subvalue.
To display the value of the environment variable as a single text string, unselect the SPLIT check box. When SPLIT is unselected, multiple values are joined together with the path separator character that is used by your operating system. This is ; (semi-colon) on Windows, and : (colon) on Unix, Linux or Mac OS X:
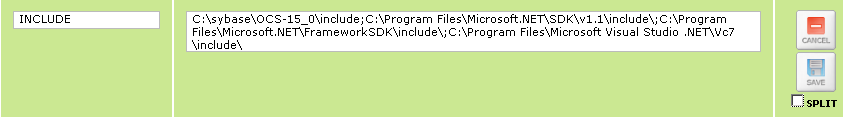
If you want to add additional subvalues to an environment variable that has only one value defined for it, select the SPLIT check box, and then type each subvalue on a separate line of text.
If the environment variable that you have edited is defined by your operating system, it is displayed in italics on the Environment Variables screen:
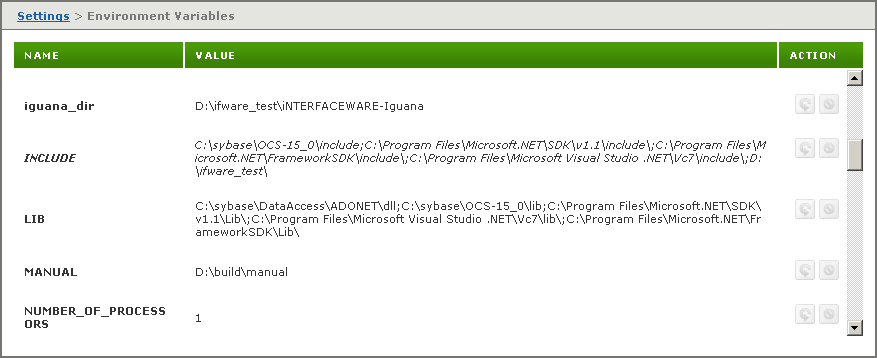
To use the value of a previously defined environment variable as a value or subvalue of the environment variable that you are editing, use ${VAR}, replacing VAR with the name of the previously defined variable:

The Previously Defined Environment Variable

Using the Previously Defined Variable In Your Edited Environment Variable
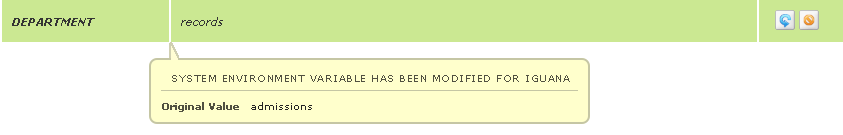
If you have used Iguana to change the value of an environment variable that is defined outside Iguana, you can use ${system#VAR} to specify that the original value of the environment variable is to be used:
The Redefined Environment Variable
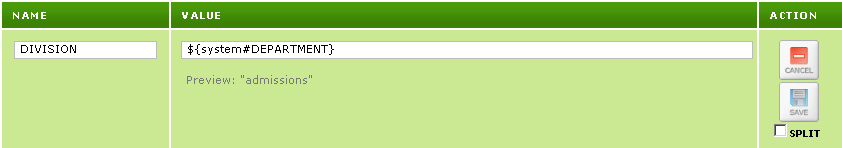
Using the Original Value of the Redefined Environment Variable
You can also use ${system#VAR} to append a value to an environment variable that is defined on your system. For example, the following adds the directory D:\build to your Path environment variable:
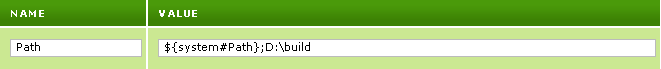
To revert to the original value of the environment variable, move your cursor over
the environment variable and click
 .
.